Imbalance hormonal
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling with weight gain despite your efforts to eat healthily and exercise regularly? Hormonal imbalances could be the cause. These imbalances, especially those related to insulin, can lead to metabolic disorders and make it difficult to lose weight. In this article, we will explore the relationship between hormonal imbalances and weight gain in insulin, their effects on metabolic disorders and how to manage them.
Understanding Hormonal Imbalances
Whether you are male or female, hormonal imbalances can affect your body’s weight, causing fluctuations in appetite, cravings, and metabolism. The endocrine system, which secretes hormones, plays a crucial role in maintaining your body’s balance and homeostasis. However, hormonal imbalances can occur due to several reasons, including stress, poor lifestyle choices, diseases, and chronic conditions.
What is Insulin?
Insulin is one of the most critical hormones that regulate your body’s energy usage. It is produced in the pancreas and helps your body use sugar (glucose) from food for energy or store it for later. However, insulin levels can get imbalanced, leading to weight gain, insulin resistance, and eventually diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Impact of Hormonal Imbalances on Weight Gain and Metabolic Disorders
Hormonal imbalances can lead to insulin resistance, where your cells become resistant to insulin. This results in your pancreas producing more insulin, leading to weight gain as excess sugar is stored as fat. This resistance can also cause inflammation, high blood pressure, and other metabolic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
My Experience with Hormonal Imbalances
As a woman, I struggled with hormonal imbalances that caused sudden weight gain, acne, and mood swings. It was frustrating to watch my weight go up despite eating healthily and working out. After consulting with my doctor, I discovered that I had insulin resistance, which made it difficult for me to lose weight. With the help of dietary changes, exercise, supplements, and medication, I was able to manage my hormonal imbalances and lose the excess weight.
Managing Hormonal Imbalances for Weight Loss
The first step to managing hormonal imbalances is to identify the root cause. Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, stress management, and a nutrient-rich diet can help regulate insulin levels and lead to weight loss. Supplements such as magnesium, vitamin D, and chromium can also help balance hormones. Medications such as Metformin can help reduce insulin resistance and increase weight loss.
Changes to Your Diet
Consuming a nutrient-rich, low-glycemic diet can help regulate insulin levels and aid weight loss. Include high-fiber foods, lean protein, and healthy fats in your diet. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), flaxseeds, and chia seeds, help reduce inflammation and regulate hormones. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, caffeine, and alcohol, which can spike insulin levels.
Exercise and Stress Reduction
Regular exercise and stress reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help regulate insulin levels and manage hormonal imbalances. Exercise helps burn excess fat and increase muscle mass, leading to weight loss. It also reduces stress hormone levels such as cortisol, which can negatively impact insulin regulation.
Question and Answer
Q1: What are the common symptoms of hormonal imbalances?
A1: The common symptoms of hormonal imbalances include weight gain, fatigue, hair loss, acne, mood swings, and irregular menstrual cycles.
Q2: How can you test for hormonal imbalances?
A2: Hormonal imbalances can be tested through blood tests, saliva tests, or urine tests that measure the levels of specific hormones in the body.
Q3: Can hormonal imbalances lead to infertility?
A3: Yes. Hormonal imbalances, especially those related to insulin resistance and PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome), can lead to infertility in women.
Q4: Can Hormonal imbalances be cured?
A4: Hormonal imbalances can be managed and treated through appropriate lifestyle changes, medication, and supplements. However, the cure depends on the severity and root cause of the imbalance.
Conclusion of Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain in Insulin and its Relationship to Metabolic Disorders
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact your body’s weight and lead to metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance and diabetes. Identifying the root cause and making appropriate lifestyle changes can help manage these imbalances, regulate insulin levels, and aid weight loss. Consult your doctor to discuss your options and create a personalized plan to manage hormonal imbalances and achieve optimal health.
Gallery
Can Hormonal Imbalance Cause Weight Gain? - Five Spot Green Living

Photo Credit by: bing.com / imbalance hormonal
What Happens To Your Body When You Suffer From Hormonal Imbalance
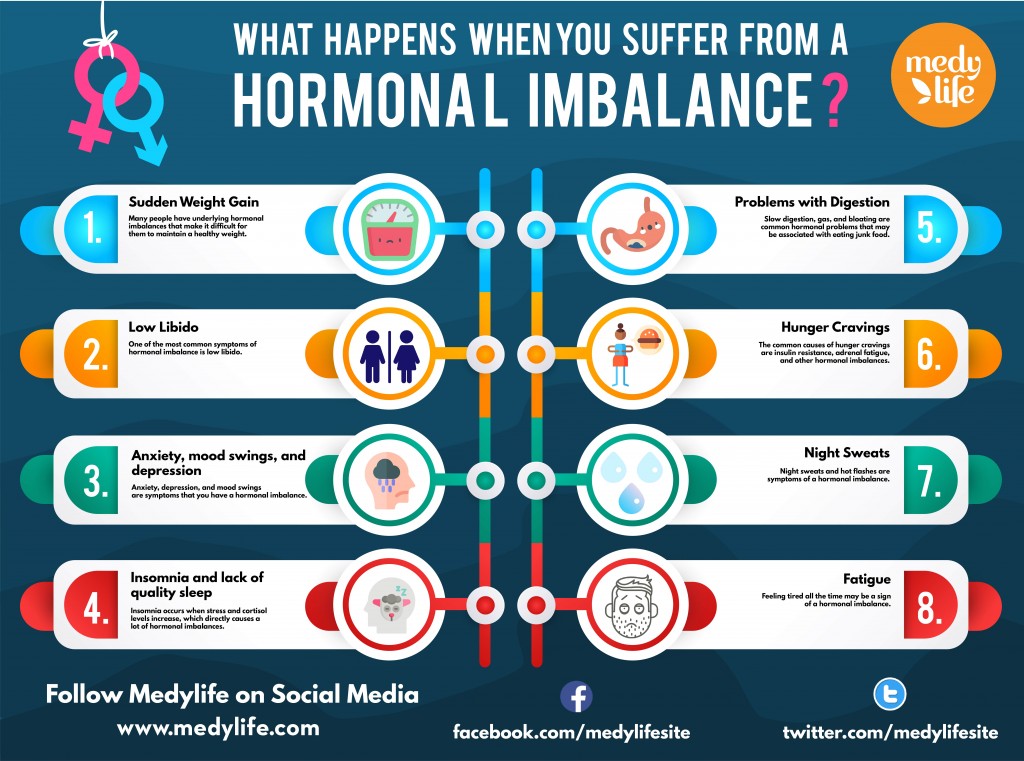
Photo Credit by: bing.com / imbalance hormonal happens when suffer men hormones female male body fact too
How To Balance Hormones Naturally - Colleen Christensen Nutrition

Photo Credit by: bing.com / hormones imbalance hormonal ranging imbalances autoimmune dietary
Hormonal Imbalance: Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment

Photo Credit by: bing.com / imbalance hormone symptoms hormonal causes effects problems treatment
Hormonal Imbalances Cause Weight Gain: The Hidden Truth!

Photo Credit by: bing.com / imbalances hormonal





