How blood sugar levels may mean the difference between weight gain and
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling with weight gain and wondering why diets and exercises do not seem to work for you? It might be more than just a lack of willpower. Hormonal imbalances can play a significant role in weight gain, especially when it comes to insulin and blood sugar control.
Understanding the Pain Points Related to Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain in Insulin and Blood Sugar Control
Are you feeling frustrated that you have tried everything, yet you cannot seem to shed off those extra pounds? Do you experience low energy levels, frequent mood swings, and sugar cravings? These could be signs of hormonal imbalances affecting your insulin and blood sugar control, leading to weight gain.
Target of Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain in Insulin and Blood Sugar Control
Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate many bodily functions. Insulin and blood sugar control, in particular, play a critical role in determining if you will gain or lose weight. Insulin is produced by the pancreas and regulates how the body uses and stores glucose from food. When insulin levels are high, the body tends to store more fat, leading to weight gain. Hormonal imbalances can cause insulin resistance, meaning that the body cells become resistant to insulin’s effects, leading to high blood sugar levels and weight gain.
Summary of the Main Points Related to Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain in Insulin and Blood Sugar Control
If you are struggling with weight gain, it is important to consider hormonal imbalances that affect insulin and blood sugar control. Such imbalances can cause insulin resistance resulting in high blood sugar levels and weight gain. Symptoms of hormonal imbalances include low energy levels, mood swings, and sugar cravings. To address this issue, it is essential to optimize insulin and blood sugar levels by adopting lifestyle habits such as exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management.
Personal Experience with Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain in Insulin and Blood Sugar Control
After years of struggling with weight gain, I was diagnosed with insulin resistance, and it all started to make sense. I used to have low energy levels throughout the day and could not control my sugar cravings, which only made things worse. However, once I understood that hormonal imbalances were the root cause of my weight gain, I started making lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management practices. Gradually, I began to see the results, and now I feel much healthier and happier.
Why Hormonal Imbalances Affect Insulin and Blood Sugar Control
Hormonal imbalances can affect insulin and blood sugar control by decreasing insulin sensitivity, leading to insulin resistance. High blood sugar levels resulting from insulin resistance also lead to weight gain. Lifestyle choices such as a poor diet, lack of exercise, and high-stress levels can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, leading to more weight gain.
The Role of Diet in Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain in Insulin and Blood Sugar Control
Diet plays a critical role in insulin and blood sugar control. Consuming high glycemic index foods such as refined carbohydrates, sugary drinks, and processed foods can increase insulin and blood sugar levels, leading to weight gain. Adopting a balanced diet that includes fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels and control weight gain.
FAQs: Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain in Insulin and Blood Sugar Control
What are the common signs of hormonal imbalances affecting insulin and blood sugar control?
Some of the common signs include low energy levels, frequent mood swings, sugar cravings, weight gain, and difficulty losing weight despite exercise and diet.
Can hormonal imbalances be treated?
Yes, hormonal imbalances can be treated with lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and medication in severe cases.
How does stress affect hormonal imbalances and weight gain in insulin and blood sugar control?
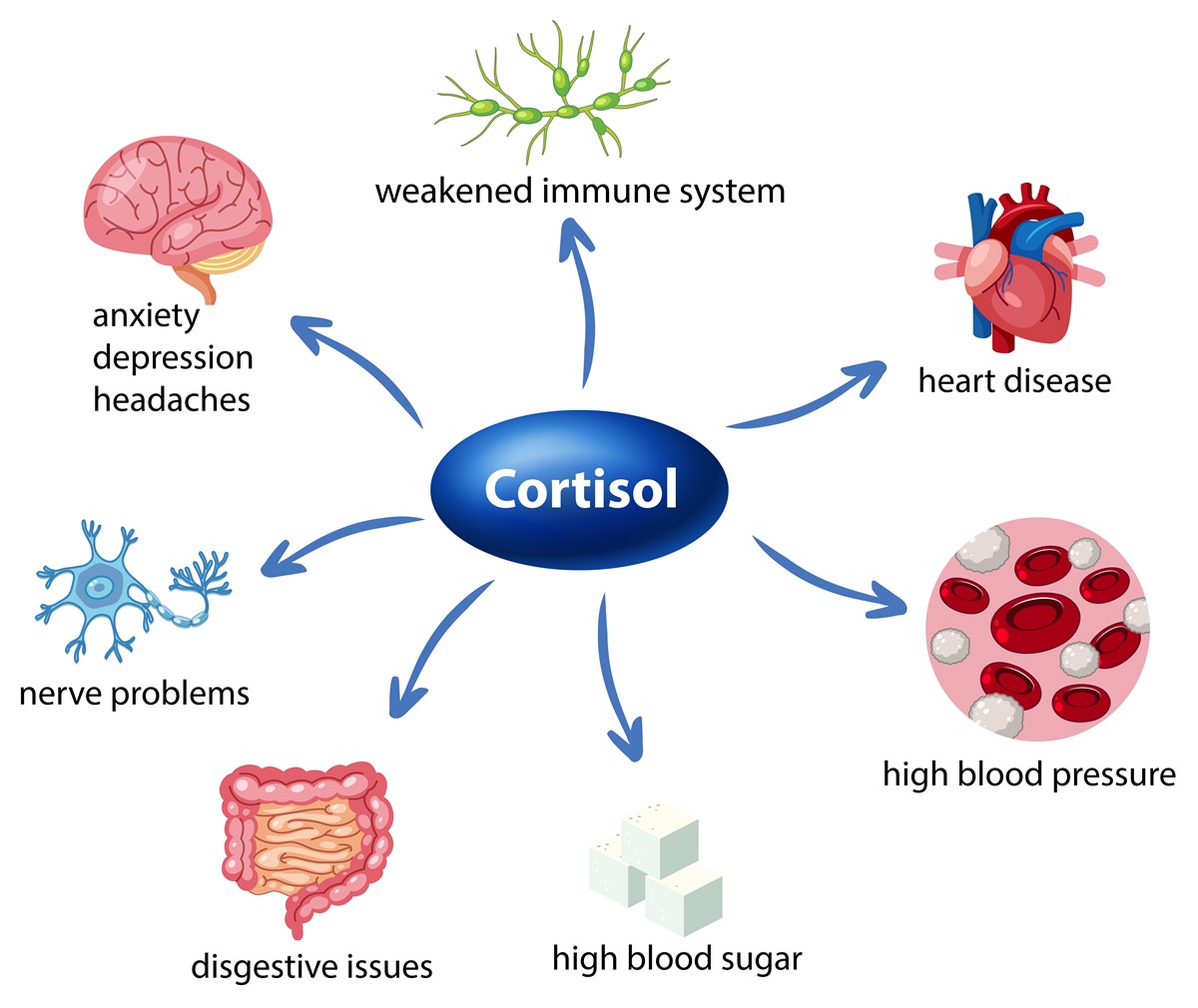
Stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances by increasing cortisol levels, which can lead to insulin resistance, high blood sugar levels, and weight gain.
Why is it important to address hormonal imbalances that affect insulin and blood sugar control?
Hormonal imbalances can cause weight gain, which can lead to other health issues such as obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. Addressing hormonal imbalances can help regulate blood sugar levels, control weight gain, and improve overall health.
Conclusion of Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain in Insulin and Blood Sugar Control
Hormonal imbalances can cause weight gain, especially when it comes to insulin and blood sugar control. Symptoms of hormonal imbalances include low energy levels, sugar cravings, and mood swings. Adopting lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help regulate insulin and blood sugar levels, control weight gain, and improve overall health.
Gallery
Graphixlogodesign: What Helps Hormonal Imbalance

Photo Credit by: bing.com / imbalance hormone hormonal tiba ereksi sering pills imbalances
How Blood Sugar Levels May Mean The Difference Between Weight Gain And
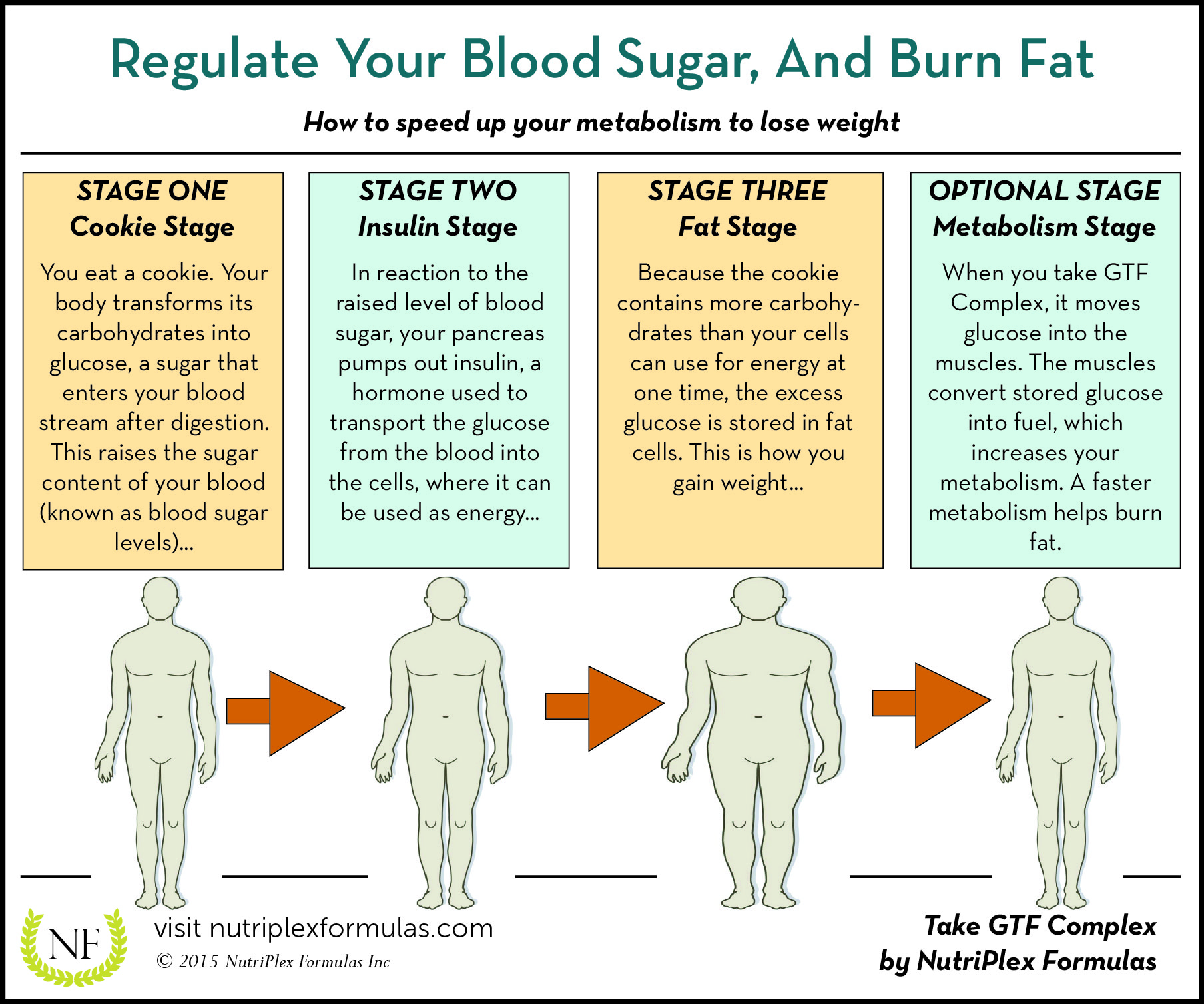
Photo Credit by: bing.com / sugar blood weight levels gain loss between difference mean infographic regulate window enlarge click
Pin On GF, DF, SF

Photo Credit by: bing.com / insulin gain estrogen menopause dominance metabolic
Hormonal Imbalance: Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment

Photo Credit by: bing.com / imbalance hormone symptoms hormonal causes effects problems treatment
Hormonal Imbalances Cause Weight Gain: The Hidden Truth!

Photo Credit by: bing.com / imbalances hormonal